How to Identify Pod and Stem Blight
Pod and stem blight manifests through several key symptoms, which differ based on the plant's growth stage.
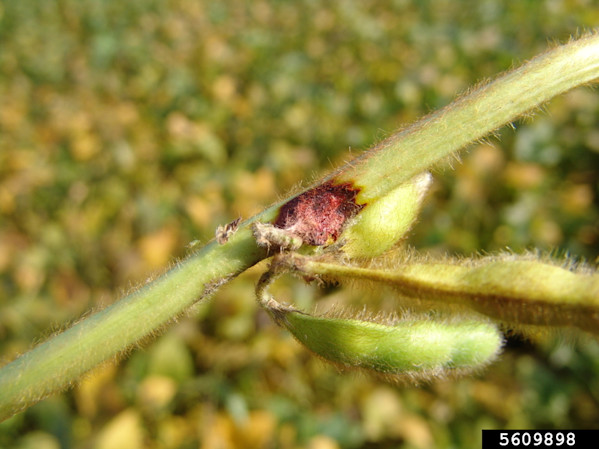
The most distinctive symptom of pod and stem blight is the emergence of small, black, elongated lesions on the stems, pods, and petioles. These lesions are the fungus's reproductive structures, known as pycnidia. They often arrange themselves in rows or bands, creating a rough, sandpaper-like texture on the stem.
In the early stages, the disease may induce wilting and yellowing of leaves. As it advances, it can cause premature defoliation and plant death. Infected pods typically contain shriveled seeds, possibly covered with a chalky, white mold.
(Image Credit: Gerald Holmes, Strawberry Center, Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, Bugwood.org)