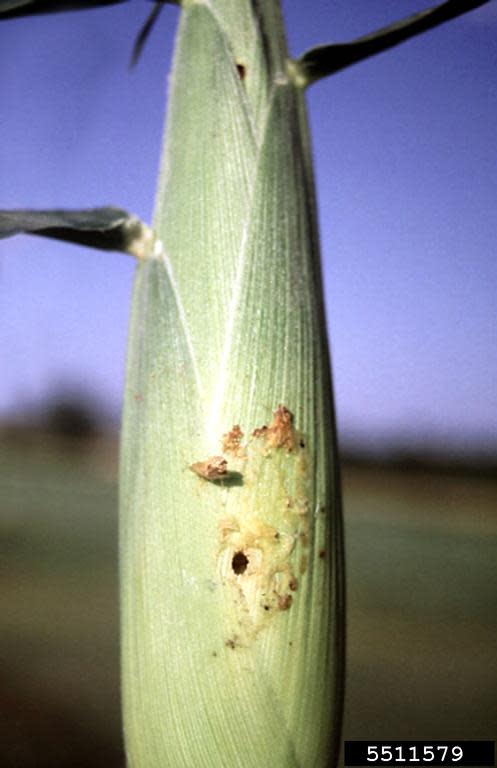
© 2014 - 2024 Farmer's Business Network, Inc. All rights Reserved. The sprout logo, “Farmers Business Network”, “FBN”, “FBN Direct” are trademarks or registered trademarks of Farmer's Business Network, Inc. This content was written by Norm℠, reviewed and edited by Mikaela Tierney.
Viptera™ is a trademark of Syngenta Group Company.
Agrisure® is a registered trademark of Syngenta Group Company.
*Asana® XL is a restricted use pesticide.
Asana is a registered trademark of Valent U.S.A. Corporation.
*Willowood Lambda-Cy 1EC is a restricted use pesticide.
*GCS Bifenthrin 2EC is a restricted use pesticide.
*RESTRICTED USE PESTICIDE Due to acute toxicity. For retail sale to and use by certified applicators only – NOT to be used by uncertified persons working under the supervision of a certified applicator.
FBN Direct products and services and other products distributed by FBN Direct are offered by FBN Inputs, LLC and are available only in states where FBN Inputs, LLC is licensed and where those products are registered for sale or use, if applicable. If applicable, please check with your local extension service to ensure registration status. Nothing contained on this page, including the prices listed should be construed as an offer for sale, or a sale of products. All products and prices are subject to change at any time and without notice and excludes CA mills tax and MN ACRRA fees. Terms and conditions apply.